Retina Conditions
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that can cause vision loss and blindness in people who have diabetes. It affects blood vessels in the retina (the light-sensitive layer of tissue in the back of your eye). In some people with diabetic retinopathy, blood vessels may swell and leak fluid. In other people, abnormal new blood vessels grow on the surface of the retina. The retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. A healthy retina is necessary for good vision. If you have diabetic retinopathy, at first you may not notice changes to your vision. But over time, diabetic retinopathy can get worse and cause vision loss. Diabetic retinopathy usually affects both eyes. How does diabetic retinopathy cause vision loss? Blood vessels damaged from diabetic retinopathy can cause vision loss in two ways: 1. Fragile, abnormal blood vessels can develop and leak blood into the center of the eye, blurring vision. This is proliferative retinopathy and is the fourth and most advanced stage of the disease. 2. Fluid can leak into the center of the macula, the part of the eye where sharp, straight-ahead vision occurs. The fluid makes the macula swell, blurring vision. This condition is called macular edema. It can occur at any stage of diabetic retinopathy, although it is more likely to occur as the disease progresses. About half of the people with proliferative retinopathy also have macular edema. Anti-vegf injections, laser and surgery may be indicated to treat different stages of diabetic retinopathy. Information provided courtesy of the US National Institutes of Health, National Eye Institute.
To learn more, please ask our doctors, or visit https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases |
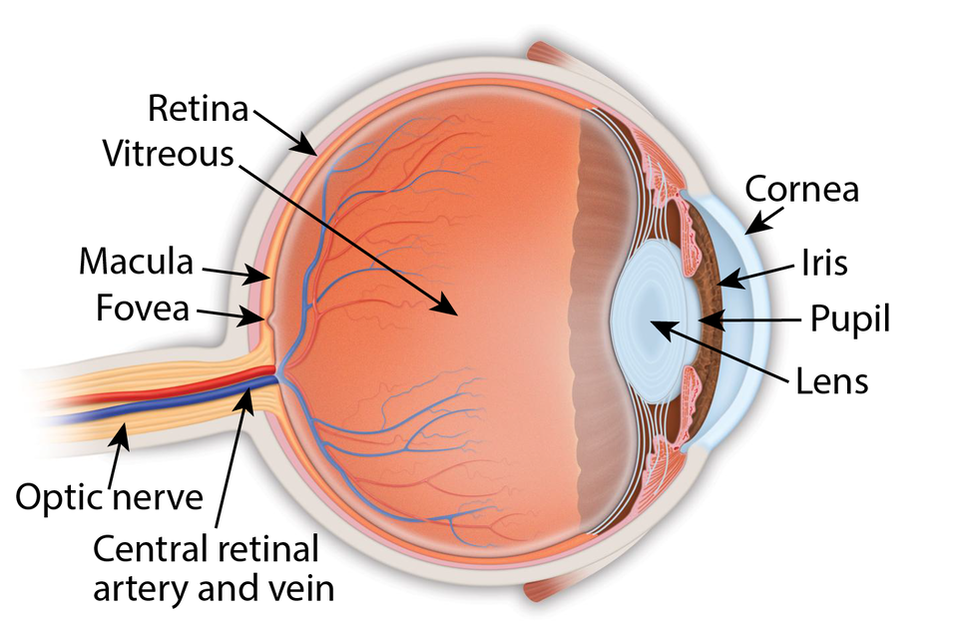
Eye Anatomy
Retina: the light-sensitive membrane in the back of the eye that converts light to electrical impulses that are sent to the brain through the optic nerve
Vitreous: also called vitreous humor, a thick, colorless gel that fills the large space in the middle of the eye, behind the lens Macula: the central retina that contains the fovea Fovea: a shallow pit in the center of the retina responsible for our sharpest straight ahead vision Optic nerve: carries the message of vision from the retina to the brain Cornea: transparent convex membrane that covers the pupil and iris of the eye Iris: colored part of the eye that consists of a muscular diaphragm surrounding the pupil and regulates the light entering the eye by expanding and contracting the pupil Pupil: dark circular opening at the center of the iris in the eye, where light enters the eye Lens: focuses light to produce an image on the light-sensitive cells of the retina. Nearly spherical and convex on both sides, it sits behind the pupil |
|
Copyright © 2021 Retina Consultants. All rights reserved.
|